lv mv | westinghouse Lv mv products lv mv Different Types of Voltage Level: The different type of voltage notations is being used in a power system transmission and distribution. Let see the type of voltage. Rated Voltage. Nominal Voltage. Extra-low Voltage. The Cosmopolitan of Las Vegas hotel rooms are spacious, warm and welcoming, with artful, hand-crafted touches that give each space the intimate feel of a private urban residence. Urban elegance. City Room. An elegant urban residence in the heart of The Las Vegas Strip. Book It. Learn More. Stunning design, eclectic charm. .
0 · westinghouse Lv mv products
1 · mv Lv substation
2 · mv Lv meaning
3 · mv Lv electrical
4 · difference between hv and Lv
5 · Lv mv equipment
6 · Lv mv drives
7 · Lv and mv electrical equipment
Underscored by a luxury design ethos, the COS women's clothing collection pays meticulous attention to sustainable craftsmanship, premium materials and a superior colour palette.
Different Types of Voltage Level: The different type of voltage notations is being used in a power system transmission and distribution. Let see the type of .
MV: 4kV to 35kV.
westinghouse Lv mv products
mv Lv substation
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a .Different Types of Voltage Level: The different type of voltage notations is being used in a power system transmission and distribution. Let see the type of voltage. Rated Voltage. Nominal Voltage. Extra-low Voltage. MV: 4kV to 35kV. This technical article will explain the most common power supply for LV networks provided by an MV/LV transformer. Don’t be confused, the same transformer with or without some modifications can be used also as a backup power supply, special power supply for safety services, or auxiliary power supply. Let’s see the most common power supply .
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards. As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2-Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V . Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay.High Voltage - 35kV to 230 kV. Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here.
Low Voltage (LV): up to 1000V. Medium Voltage (MV): between 1000 V and 45 kV. High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above.When it comes to electrical cables, there are two main types: low voltage (LV) and medium voltage (MV) cables. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is important for anyone working with electrical systems. “3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.
Different Types of Voltage Level: The different type of voltage notations is being used in a power system transmission and distribution. Let see the type of voltage. Rated Voltage. Nominal Voltage. Extra-low Voltage. MV: 4kV to 35kV. This technical article will explain the most common power supply for LV networks provided by an MV/LV transformer. Don’t be confused, the same transformer with or without some modifications can be used also as a backup power supply, special power supply for safety services, or auxiliary power supply. Let’s see the most common power supply .
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards. As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2-Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V . Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay.High Voltage - 35kV to 230 kV. Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here.
mv Lv meaning
Low Voltage (LV): up to 1000V. Medium Voltage (MV): between 1000 V and 45 kV. High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above.When it comes to electrical cables, there are two main types: low voltage (LV) and medium voltage (MV) cables. Understanding the differences between these two types of cables is important for anyone working with electrical systems.


mv Lv electrical
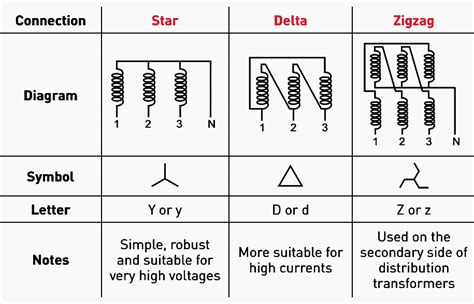
difference between hv and Lv
Lv mv equipment
Lv mv drives
Our studies reveal a new molecular glue that recruits its target protein directly to DDB1 to bypass the requirement of a substrate-specific receptor, presenting a new strategy for targeted protein degradation. Keywords: CDK12/CCNK; biochemistry; chemical biology; human; molecular glue; target identification; targeted protein degradation.
lv mv|westinghouse Lv mv products